Are you ready for the next generation of mobile connectivity? If you are a part of the technology industry, you are likely familiar with the roll-out of the next generation of mobile tech and what it means for the future of technology and communications. For those who aren’t, there is an exciting development in mobile generations currently spreading its way across the globe, reaching into all major UK cities and large town locations - the introduction of the 5G mobile network.
What is 5G?
The 5G network is the next generation of mobile connectivity and comes with a promise of faster speeds, greater latency and an improved capacity for connections. It works in the same way as 4G, making use of signals carried on radio waves that are transmitted between radio masts or antennas and your mobile phone.
However, 5G networks differ in that the waves are at a much higher frequency. While this allows for a greater number of connected devices with less drop-out, the waves are restricted in the distance they can travel, especially in built-up areas, and require a greater number of masts that are closer to the ground in order to maintain a strong connection.
5G is expected to be available across the vast majority of developed countries by the end of 2020. However, when you consider that 4G is still to be introduced to some rural areas in the UK, whether this goal is achievable stands to be seen.
Why is 5G a Big Deal?
As 5G becomes more widely available, we will start to see drastic improvements across internet-connected devices, covering a wide variety of technology from self-driving cars and smart home appliances to health and safety technologies and superfast mobile broadband that almost does away with the need for landlines altogether.
Additionally, anticipated smartphone numbers are expected to reach over 6 billion by 2020.
Ultimately, this means there will be a lot more users browsing online from their phones and businesses will need to ensure they are offering both an efficient online experience and working harder to connect their online presence with real-world customer service to accommodate this.
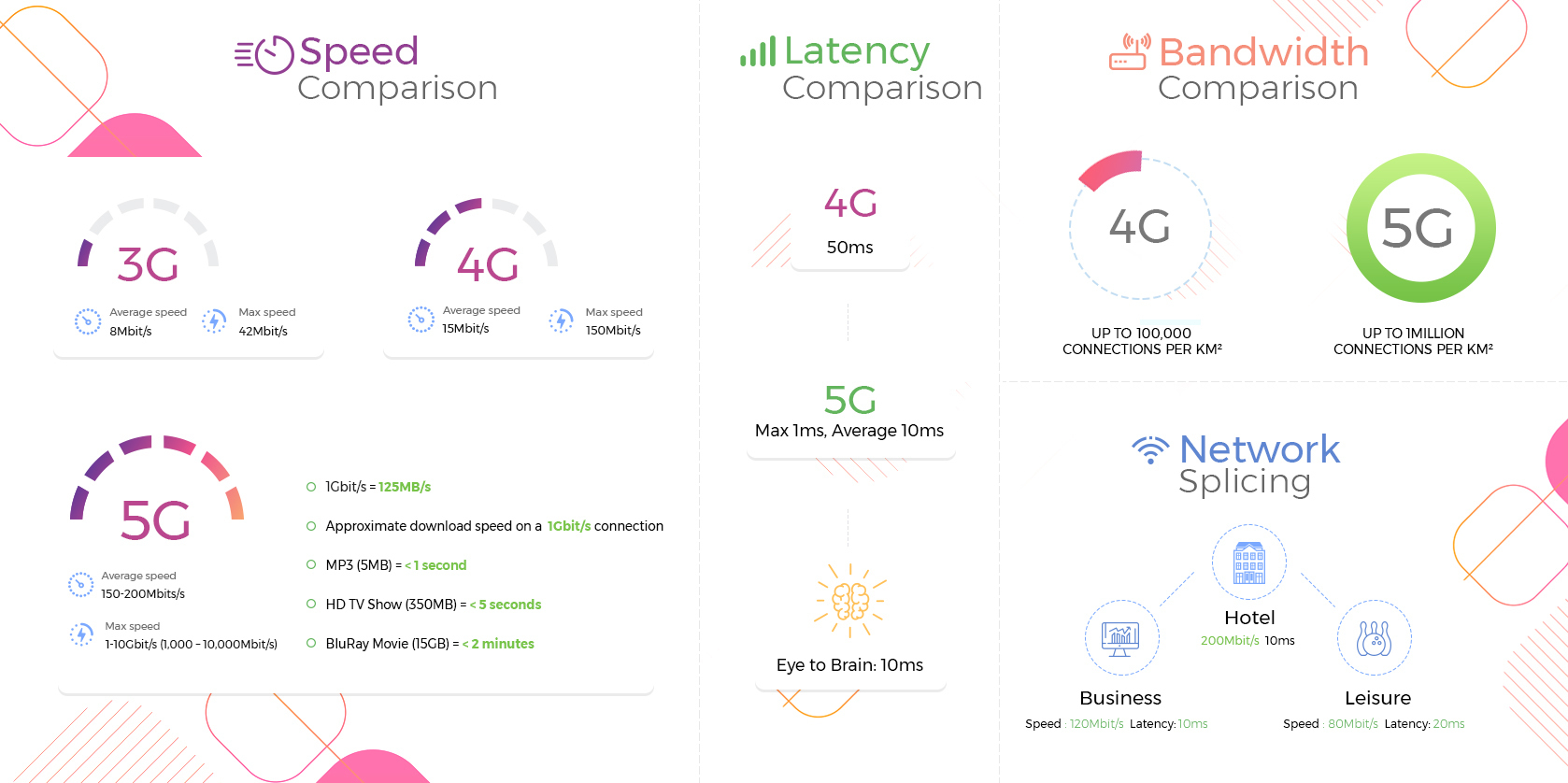
5G will offer peak speeds that can support up to an amazing 10Gbps, over 1000x what 4G is capable of currently. That doesn’t mean you should instantly head out to your nearest mobile phone supplier for a 5G enabled device based on this figure, however, as all networks will be capped about 10x less in the initial stages of rollout. That being said, EE are estimating speeds of 1Gbps and Three are offering up to 2Gbps on their home-broadband package.
Remember, a Gb (GigaBIT) is not the same as a GB (GigaBYTE)! To contextualise just how fast 5G will be:
- 1Gbps in connection speed is approximately a download speed of 125MB per second, allowing you to
o download a standard 5MB MP3 track in under a second
o download a 350MB HD TV Show in 3-5 seconds, and
o download a 15GB Blu-Ray movie in under two minutes.
With 5G connections comes an improved latency or reduced lag. This is a measurement of the time it takes data to be received at the end destination. To best explain this, consider the process of sending a parcel by registered mail. One-way latency is the time taken for the parcel to go from the sender’s hands to the receiver’s hand. While the round-trip latency is the time between the sender handing over their parcel and the sender then receiving confirmation of the delivery having been made.
By improving both these latency response times, we can see events closer to real-time, such as streamed sports games and concerts and use this faster receipt of information in aspects of safety, such as the highly important decisions made by self-driving cars. Currently, response times on 4G connections are up to 50 milliseconds, while 5G is expected to have a latency of 1millisecond, an improvement of 50x that of 4G.
However, it could be some time before real-world tests show latency times as small as this and the average expected latency on 5G will be around 10ms. In comparison, that is the same amount of time it takes our brains to process information sent from our eyes.
Another excellent advancement with the introduction of 5G connections is increased bandwidth or the greater capacity for simultaneous connections. Currently, while connection speeds are strong in built-up areas and busy cities, the quality of the connection is poor, with many users facing buffering videos and long page-load times. This is due to a restriction on 4G connections for up to 100,000 devices per square kilometre. As 5G rolls out, it’s expected to confidently handle up to 1million connections in every square kilometre, vastly improving connections and services in large business areas and highly populated residential areas.
Expected to be a critical component of the 5G offering, network slicing allows for the creation of multiple virtual networks from a common shared physical infrastructure. These virtual networks can be tailored specifically to different requirements, whether it’s an appliance, customer or device and provide greater cost and energy efficiencies than previous mobile network generations.
Each virtual network that is created can have the speed, capacity, bandwidth and coverage set according to the needs of the connection, completing isolating it from other connections with no interference from traffic received on the common infrastructure. Those using the split virtual network will experience no visible or usage differences, as though they were on their own separate physical connection.
What Will Be Improved by 5G?
While it might seem like the greatest benefit of 5G will be the internet speeds achievable, there is so much more to this next leap in mobile generations that will lead to a smarter, more connected world. Including but not limited to;
These technologies have been around in some application for decades, however, it’s only in recent years that they’ve developed enough to be an affordable entertainment option for home use.
VR or Virtual Reality allows users to immerse themselves in a three-dimensional virtual world, typically by wearing suitably designed VR technology such as a helmet and motion controllers. VR has seen plenty of use across the film and games industries but also has applications in training specific roles such as surgeons and engineers.
AR or Augmented Reality is a similar technology to Virtual Reality, however, it allows users to see a blended vision of digital aspects mixed with real-world surroundings. The best example of this is the popular mobile phone game Pokémon Go, which sees users exploring out in the real world looking for digital pocket monsters to capture. Once found, users can use their phone camera to ‘see’ their Pokémon in the real world and take pictures to share with friends and online. Further recent uses of AR have included Google’s recent Animal AR Search feature and furniture placement apps used by Made.com and IKEA.
Both VR and AR have been held back by available connectivity and with the introduction of 5G will see these technologies quickly reach their full potential and see users enjoying fully virtual or augmented worlds without nausea-inducing lag, jerky dropped frames and lost connections. As 5G becomes more widely available, VR and AR technologies will become smaller, more cost-effective and seamless, offering truly immersive experiences.
This isn’t the first-time smart cities have been talked about in the UK and while Bristol was announced as the UK’s smartest city in 2017, truly smart cities are yet to be strictly defined and are still, currently, a dream for tomorrow’s world. As 5G rolls out beyond the major cities in the UK, smarter cities could quickly become a reality, with smart bins, streetlights and water meters introduced in highly populated areas.
Not only will this save councils on costs and staff resources, in a report released by mobile network O2 in 2018, but figures also suggested the greater availability of 5G connections in domestic households could see savings up to £450 a year across energy bills, council tax and food costs. The savings don’t stop there! As 5G is utilised by the NHS and healthcare services, an estimated 1.1million GP hours could be freed up through the use of remote health services and smart wearables that monitor a patient’s health and vital signs.
Have you ever been watching a live sports event and just before something climactic happens, you’ve heard a loud cheer or a groan from a nearby property or pub? Only to see the source of their joy or pain in the game a few seconds later. 5G will eliminate this viewing lag, allowing events to be watched in seemingly real-time and enabling broadcasters to use fewer resources and equipment to stream their content.
Additionally, 5G’s support of VR and AR applications will make it easier for viewers to immerse themselves into the event, able to watch the game or concert through their home virtual reality set-ups as if they were truly attending! This will also facilitate augmented reality applications for those seated at the event, providing options to view instant replays.
Unlike self-driving cars that are still many years from becoming a real-world reality, connected cars are currently on the market and have made impressive leaps in technological advances. The use of internal communications that can tell the car to adjust its wiper speed, suspension control and other applications such as lights, ABS and power steering, depending on speed and weather and road conditions have made cars more fuel and energy efficient for drivers and helped to reduce individual carbon footprints.
In addition to making vehicles cleaner on the roads, connected car technology can help to complement smart city services with V2V and V2X technology, also known as ‘Vehicle to Vehicle’ and ‘Vehicle to Everything’ communication. Cars will be able to monitor and feed data back to traffic infrastructures on road conditions, traffic build-ups and environmental surroundings, informing drivers of improved routes that are safer for their car or quieter routes that avoid congestion. The future applications of V2V and V2X communications are limitless, allowing cars to monitor street services such as waste bin collection, notify authorities on roads that require repair and inform other drivers on available parking, as a few examples.
Another exciting technology of tomorrow’s world, self-driving cars are currently being used in real-world testing however still have plenty of time and development before they can be used in a commercial setting. 5G will assist with the development of safer self-driving or autonomous cars that can react faster in real-time, avoiding sudden hazards and making smarter choices, such as using backroads in reaction to an accident or sudden congestion.
As 5G not only allows for greater download speeds and a higher capacity of connected devices, the vast improvement in latency will be the most useful feature of 5G connectivity in autonomous cars. Useful real-time data can be sent to self-driving cars including available parking spaces, city pollution levels and potential road hazards, making journeys smoother, safer and reducing inconvenience.
The Internet of Things has been in active use since 2017 and is commonly used for household appliances such as heating thermostats, lighting and coffee machines and is slowly rolling out to include larger appliances such as fridges, washing machines and even cookers, too. As the name suggests, the IoT is the process of connecting devices to the internet allowing them to be controlled remotely, gather useful user data and react in real-time to external circumstances.
The best example of how the Internet of Things-enabled devices have made life more cost-effective and efficient are smart thermostats. Initially, smart thermostats could simply be adjusted remotely, allowing you to turn your heating on from your smartphone before arriving home from work, or turn it off after you left the house.
Today’s modern smart thermostats have greater advanced features, including active monitoring of current devices. This means that your heating system knows when you have left and will automatically turn the heating off, and knows when you are on your way home and will warm the house for your arrival. Learning thermostats will gradually begin to understand your routine, turning the heating down when you go to bed and monitoring outdoor temperatures and weather conditions to adjust internal temperatures accordingly.
Earlier, we briefly mentioned how 5G could free up an additional 1.1 million GP hours for the NHS using remote health services and monitoring devices. This by itself would be an amazing development, however, this is just the beginning of the benefits available through to health and safety services with 5G connectivity.
Emergency services will be able to utilise smart cars to find the fastest routes to accidents, send out medical aid via remote-controlled drones and potentially carry out surgeries anywhere in the world with remotely connected robots, regardless of how isolated the location is. As monitoring technologies advance, patients could be offered ingestible monitoring devices that allow doctors to better monitor internal functions or smart clothing that feeds data back on vitals such as heart rate, activity level and even blood-sugar levels.
These connectivity developments combined with better access to Virtual and Augmented realities and 3D printing could pave the way for a futuristic medical industry where doctors can react to physical patient data in real-time rather than rely on the patient to describe what is wrong with them. This could speed up the time it takes us to recover from illnesses and reduce the amount of spend and resources currently required for efficient health services.
Is 5G Already Available?
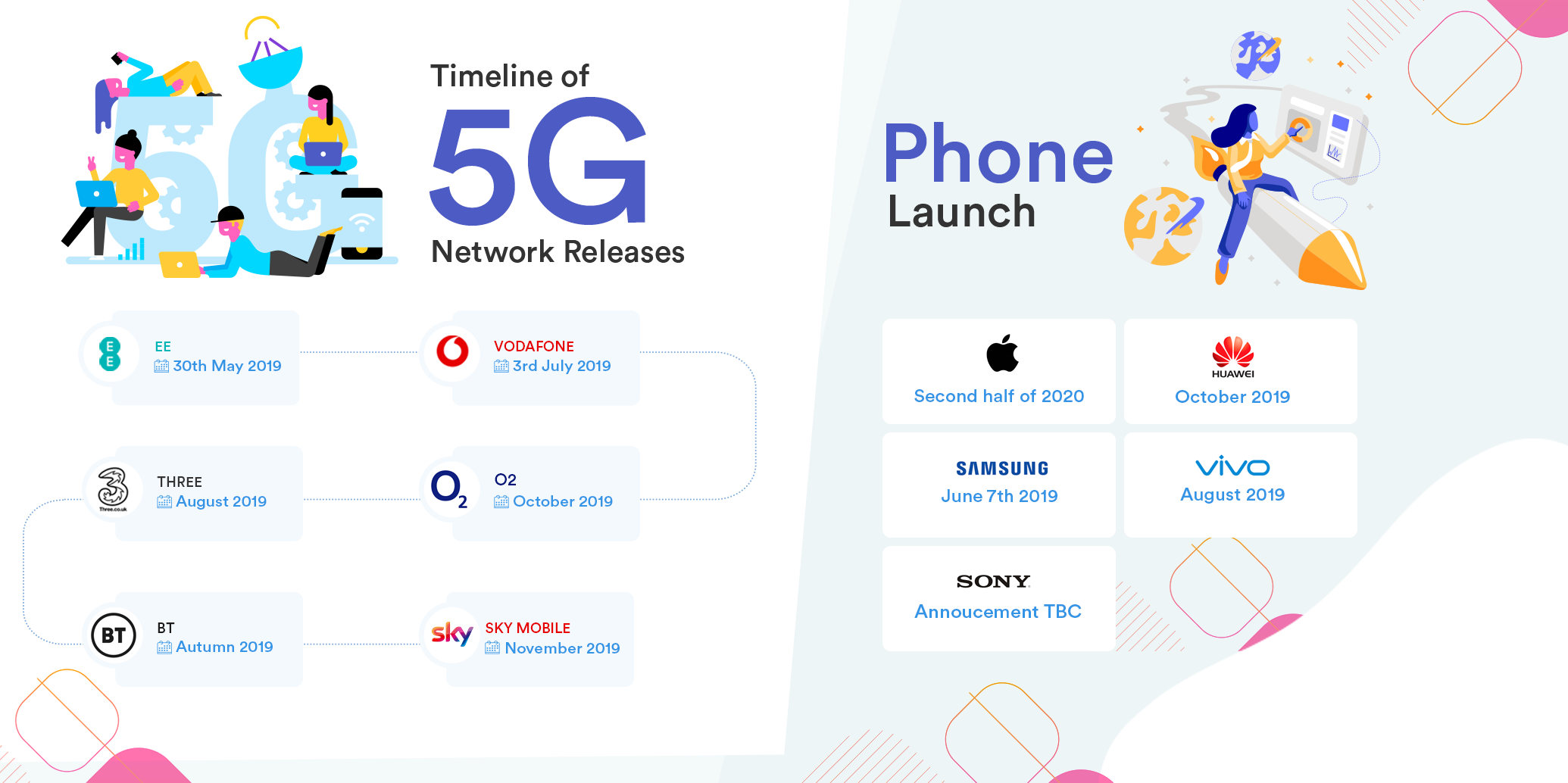
Currently, a number of the UK’s major mobile networks have announced plans to roll out 5G. Mobile network EE was the first, launching to six of the largest UK cities including London, Cardiff, Edinburgh and Belfast on the 30th May. Vodafone wasn’t far behind, launching in Birmingham, Bristol, Cardiff, Glasgow, Liverpool, London and Manchester on 3rd July and Three have announced they will be rolling out their home-broadband 5G service in London from August, although no fixed date has been given.
Where is 5G Being Used?
There are a few real-world locations that have already eagerly got behind the introduction of 5G connectivity and started to roll it out across their services or property including;
In partnership with Huawei and Shenzhen Telecom, the Intercontinental Shenzhen is the world’s first 5G smart hotel set to open in China. The hotel has advised it will offer 5G connectivity to all guests with 5G enabled smartphones and hotel experiences will include a welcoming robot, cloud-computing terminals, next-generation cloud games and cloud virtual reality rowing machines, all on the 5G network. A fixed date for when these technologies will be available to hotel guests is still to be announced but press tours were completed back in the second quarter of 2019 and were excellently received.
One of the ways how 5G connectivity is going to make big changes to remote working is the ability for huge machinery to be remotely controlled from thousands of miles away. TeleOperation is exactly that and has recently seen an excavator in South Korea controlled from a booth in Germany, an incredible distance of more than 5,000 miles. 5G was able to make this world’s first demonstration a reality by reducing the amount of lag seen on video feeds, enabling improved 3D guidance systems and providing real-time data and diagnostics to the controller that can be used to avoid danger and on-site hazards.
No longer restricted to the world of science-fiction, holographic technology has been showcased by mobile network giants EE at the 2019 British Academy of Film and Television Arts Awards held in February. Using AI (artificial intelligence), holographic technology and of course, 5G connectivity, EE created the world’s first AI Stylist, known as Shudu. The trial was intended to introduce the technology to fashion fans, show businesses how they can make use of 5G networks and provide viewers with a point of contact they can talk to via Instagram stories and use to identify fabrics, colours, patterns and entire outfits worn by celebrities. Shudu can even search online for more affordable, closely matching fashion alternatives and has been designed to uniquely tailor suggestions to individuals based on the user’s preferences.
Will I Need to Upgrade My Devices to Use 5G?
Yes. Current smartphones, smart-TVs and other internet-enabled devices are unlikely to hold the Qualcomm released 5G mobile modem. While there are already some phones that have been released to the consumer market with 5G enabled chips, it may be late 2019 - early 2020 before we start to see other 5G enabled electronics and appliances including televisions.
5G mobile phone models available now include;
- Samsung Galaxy S10 5G
- OnePlus 7 Pro 5G
- Oppo Reno 5G
- LG V50
- ZTE Axon 10 Pro 5G
Apple is one of the only leading mobile manufacturers that are yet to announce when their 5G enabled phones will be released and considering their track record for being behind the active market, a 5G enabled iPhone is unlikely to be available until 2020.
Greatest Hurdles for 5G Connectivity
The roll-out of 5G is going to massively change the world as we know it, but it’s not going to be without its challenges. The type of masts that 5G networks use can not send the signals as far as current masts, meaning more base stations will be required to cover the same area size resulting in a higher cost and a greater need for planning so not to ruin landscapes or overcrowd city spaces.
Also, there has been some backlash on the effect 5G networks can have on our health, with some medical doctors and scientists arguing that the electromagnetic radiation used in mobile phone connectivity could put users at risk of cancer. While the WHO (World Health Organisation) previously announced that all radiofrequency radiation is ‘potentially carcinogenic’, they confirmed in 2014 that "no adverse health effects have been established as being caused by mobile phone use.”
This is further supported by the type of radio waves used by mobile phone networks. Considered ‘non-ionising’ radio waves, they lack the energy required to interrupt internal body systems or cause damage to cells and have been proven to carry less energy than the light our body absorbs daily from the sun.
How 5G Will Affect the Digital Marketing Industry
We have already seen the effect that mobile-first has had on the industry and the struggle for some websites to offer fully optimised websites that load within 3 seconds across most popular devices. As 5G rolls-out across more cities and more devices can connect in densely populated areas with no visible lag, it will be easier to identify poorly optimised websites with long loading times and reduced usability. If they remain unchanged, these websites will start to see a sharp decline in traffic, and potentially their rankings, too, as visitors show less patience for loading times - particularly when using the much faster 5G connections.
Where previously a greater focus was given to creating quality content to encourage improved organic search rankings, more websites will need to invest in providing a fully mobile-optimised website that prevents infuriated and bored users. Without a website that works well across multiple devices, many visitors simply won’t make it to the content you have spent so much time and resource to create. That doesn’t mean businesses should stop producing content, however, far from it! In fact, this development should encourage companies to create more video content. The most popular type of content taken in online, with the improved connection speed and response time available, it will be much easier for online users to watch videos than ever before, without long buffering times and stuttering frames.
While mobile devices will see the most benefit from the introduction of 5G, all device connections will see a vast improvement and we anticipate an increase in the number of people using multiple devices to connect more regularly to the online world. As a result, businesses will need to ensure they do not put all their focus on mobile devices and instead dedicate resource to linking their online and real-world experiences. Ensuring that in-store services run parallel with online and that no customer choosing to use one or both channels notices a difference in the level of customer service received.
Additionally, and most beneficially for the digital marketing industry; the improved 5G connection could see a reduced use in the number of adblockers in place online. A study taking place in 2017 by AdBlock Plus and Global Web Index, showed that 33% of users blocked ads in order to speed up their device loading times. As connection speeds improve, could this potentially encourage more users to do away with ad block? Only time will tell.
In Conclusion...
The next generation in mobile connectivity is going to be one of the greatest technological leaps the world has seen for some years and will potentially pave the way for improved healthcare, provide an excellent resource for remote working and ensure our cities are the most efficient they can be. With 5G connectivity rapidly on its way and the endless opportunities it presents, have you started considering how your business can utilise the new 5G network?